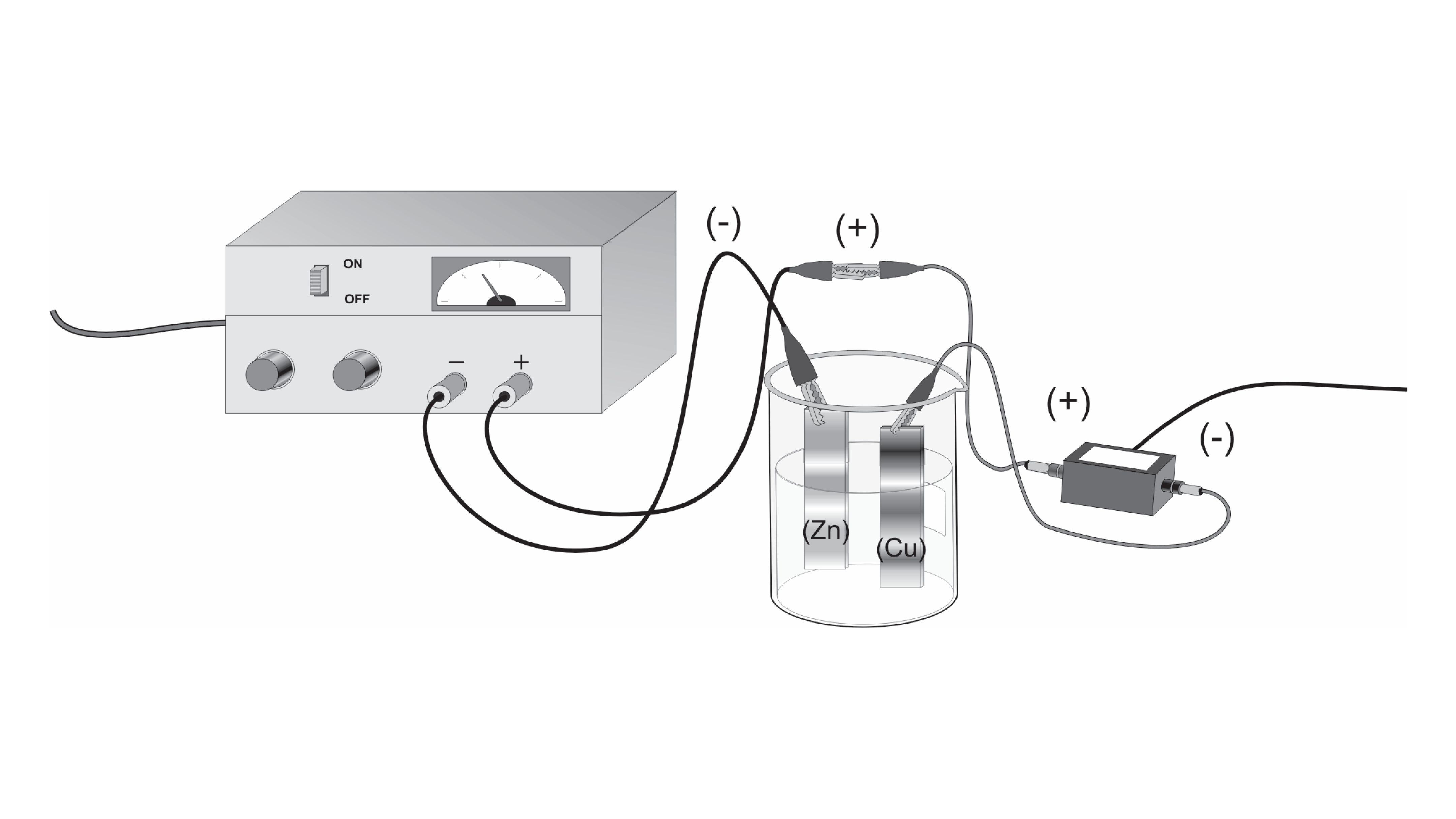
Knowing that 1 mole of copper is 63.546 grams, I should be able to get a relationship between the change in mass and the number of moles—which will give me Avogadro's number. The Avogadro constant (symbols: L, N A), also called the Avogadro number is the number of 'entities' (usually, atoms or molecules) in one mole, that is the number of carbon-12 atoms in 12 grams (0.012 kg) of unbound carbon-12 in its ground state.
Avogadro’s law, also known as Avogadro’s principle or Avogadro’s hypothesis, is a gas law which states that the total number of atoms/molecules of a gas (i.e. The amount of gaseous substance) is directly proportional to the volume occupied by the gas at constant temperature and pressure.
The Avogadro's number is a constant used in analytical chemistry to quantify the number of particles or microscopic entities from macroscopic measurements such as mass. It is very important to know this number in order to understand molecule composition, interactions and combinations. For example, to create a water molecule it is necessary to combine two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom to obtain one mole of water. The number of Avogadro is a constant that must be multiplied by the number of atoms of each element to obtain the value of oxygen (6.023 x 1023 atoms of O) and Hydrogen (2x 6.022x 1023) that form a mole of H2O.
What is the Avogadro's number?
The Avogadro's number is a constant that represents the number of existing atoms in twelve grams of 12-pure carbon. This figure makes possible to count microscopic entities. This includes the number of elementary entities (i.e. atoms, electrons, ions, molecules) that exist in a mole of any substance. The Avogadro's number is equal to (6,022 x 10 raised to 23 particles) and is symbolized in the formulas with the letters L or NA. In addition, it is used to make conversions between grams and atomic mass unit. The unit of measure of the Avogadro's number is the mole (mol-1) but it can also be defined in lb/mol-1 and oz/mol-1.
What is the Avogadro’s number?
The Avogadro’s number is 602,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 which is equal to 602,000 trillion = 6.02 x 1023. This value is found from the number of carbon atoms contained in 12 grams of carbon 12 elevated to power 23.
It is important to mention that depending on the unit of measurement used, the number may vary. In this sense, if you work with mole the number is 6.022140857 (74) x 1023 mole-1.
- If you work with pounds it will be 2.731 597 34(12) × 1026 (Lb.-mol)-1.
- If you work with ounces it will be 1.707 248434 (77) x 1025 (oz-mol)-1.
What does the Avogadro’s number represent?
The Avogadro’s number represents the number of atoms that exist in twelve grams of carbon-12.
This number represents a quantity without an associated physical dimension, so it is considered a pure number to describe a physical characteristic without dimension or explicit unit of expression. For this reason, it has the numerical value of constant that the units of measurement have.
How the Avogadro’s number is calculated
The Avogadro’s number can be calculated by measuring the Faraday constant (F) which represents the electrical charge carried by a mole of electrons and dividing it by the elementary charge (e). This formula is Na= F/e.
The Avogadro constant can be calculated using analytical chemistry techniques known as coulometry, which determine the amount of matter transformed during the electrolysis reaction by measuring the amount consumed or produced in coulombs.
There are also other methods to calculate it such as the electron mass method, known as CODATA or the system of measuring through crystal density using X-rays.

History
Explain Avogadro Number
The Avogadro’s number or Avogadro constant is named after the Italian scientist Amedeo Avogadro who in 1811 determined that the volume of a gas at a given pressure and temperature is proportional to the number of atoms or molecules regardless of the nature of the gas.

In 1909, Jean Perrin, a French physicist – winner of the Nobel Prize in physics in 1926 – proposed naming the constant in honor of Avogadro. Perrin, using several methods, proved the use of the Avogadro constant and its validity in many of his works.
Initially, it was called Avogadro’s number to refer to the number of molecules-grams of oxygen but in 1865, the scientist JohannJosef Loschmidf called the Avogadro’s number, Avogadro constant. Loschmidf estimated the average diameter of air molecules by a method equivalent to calculating the number of particles in a specific gas volume. For this reason, the particle density value of an ideal gas is known as the Loschmidt constant, which is approximately proportional to the Avogadro constant. From then on, the symbol for the Avogadro’s number or Avogadro constant can be NA (Avogadro’s number) or L (in honor of Loschmid).
A curious fact in Avogadro’s number history is that the Italian scientist Amedeo Avogadro never measured the volume of any particle in his lifetime because in his time there were no elements necessary to do so, but it is thanks to his contributions that Perrin developed this constant and therefore gave it that name.
When the weather is nice, many people begin to work on their yards and homes. For many projects, sand is needed as a foundation for a walkway, or to add to other materials. Sand could be ordered by the pound, but that takes a lot of time to weigh out. The best bet is to order sand by the yard—meaning a cubic yard. The loader can easily scoop up what the buyer needs, and put it directly into their truck.
Avogadro's Number

It certainly is easy to count bananas or to count elephants (as long as you stay out of their way). However, you would be counting grains of sugar from your sugar canister for a long, long time. Atoms and molecules are extremely small—far, far smaller than grains of sugar. Counting atoms or molecules is not only unwise, it is absolutely impossible. One drop of water contains about (10^{22}) molecules of water. If you counted 10 molecules every second for 50 years, without stopping, you would have counted only (1.6 times 10^{10}) molecules. Put another way, at that counting rate, it would take you over 30 trillion years to count the water molecules in one tiny drop.
Chemists of the past needed a name that could stand for a very large number of items. Amadeo Avogadro (1776-1856), an Italian scientist, provided such a number. He is responsible for the counting unit of measure called the mole. A mole (left( text{mol} right)) is the amount of a substance that contains (6.02 times 10^{23}) representative particles of that substance. The mole is the SI unit for amount of a substance. Just like the dozen and the gross, it is a name that stands for a number. There are therefore (6.02 times 10^{23}) water molecules in a mole of water molecules. There also would be (6.02 times 10^{23}) bananas in a mole of bananas, if such a huge number of bananas ever existed.

The number (6.02 times 10^{23}) is called Avogadro's number, the number of representative particles in a mole. It is an experimentally determined number. A representative particle is the smallest unit in which a substance naturally exists. For the majority of elements, the representative particle is the atom. Iron, carbon, and helium consist of iron atoms, carbon atoms, and helium atoms, respectively. Seven elements exist in nature as diatomic molecules and they are (ce{H_2}), (ce{N_2}), (ce{O_2}), (ce{F_2}), (ce{Cl_2}), (ce{Br_2}), and (ce{I_2}). The representative particle for these elements is the molecule. Likewise, all molecular compounds such as (ce{H_2O}) and (ce{CO_2}) exist as molecules and so the molecule is their representative particle. For ionic compounds such as (ce{NaCl}) and (ce{Ca(NO_3)_2}), the representative particle is the formula unit. A mole of any substance contains Avogadro's number (left( 6.02 times 10^{23} right)) of representative particles.
Avogadro's Number Is Useful For
Summary
- A mole of any substance contains Avogadro's number (left( 6.02 times 10^{23} right)) of representative particles.
Contributors and Attributions
Avogadro Number Is The Number Of Molecules
CK-12 Foundation by Sharon Bewick, Richard Parsons, Therese Forsythe, Shonna Robinson, and Jean Dupon.




